Top Guidelines Of Leading The Commercial 3D Printing Revolution - HP

Some Known Details About 3D Printing - SparkFun Electronics
Parts can be made rapidly and disposed of after use. Parts can also be produced in almost any geometry, which is among the core strengths of 3D printing. One of the greatest limitations of 3D printing is that the majority of parts are inherently anisotropic or not completely thick, implying they normally lack the product and mechanical homes of parts made via subtractive or developmental methods.

3d Printing: What You Need To Know
Subtractive manufacturing Subtractive manufacturing, such as milling and turning, produces items by getting rid of (machining) material from a block of solid material that's also typically described as a 'blank'. Almost any product can be machined in some method, making it a widely utilized technique. Because of Source of control over every element of the process this technique can producing extremely accurate parts with high repeatability.
The major limitation of subtractive production is that the cutting tool must be able to reach all surface areas to remove product, which restricts style intricacy quite a lot. While devices like 5-axis devices eliminate a few of these constraints, intricate parts still require to be re-orientated during the machining process, including time and cost.
Developmental production Formative production, such as injection molding and stamping, develops items by forming or molding materials into shape with heat and/or pressure. Formative techniques are designed to lower the limited cost of producing private parts, but the creation of distinct molds or devices used in the production process indicates setup expenses are extremely, very high.

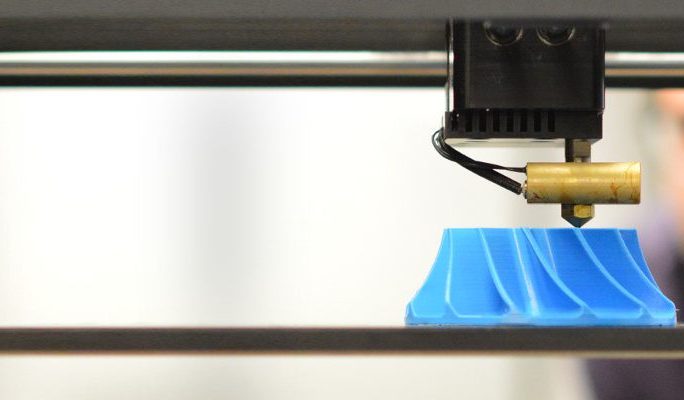
How FDM/FFF 3D Printing Technology Works? - MANUFACTUR3D
Our MakerBot: 3D Printers for Educators & Professionals PDFs
How these techniques compare Production is complicated, and there are a lot of dimensions for comprehensively comparing each technique versus all others. It is near difficult to optimize simultaneously for cost, speed, geometric complexity, materials, mechanical properties, surface finish, tolerances, and repeatability. In such complex circumstances heuristics and guidelines are more important: is best for low volumes, intricate styles, and when speed is necessary.
Cost per part is typically the governing aspect figuring out which making process is best. As a rough approximation the system costs per approach can be imagined like this: Find out more about 3D printing vs CNC machining. 3D printing is becoming cheaper every year and in some circumstances, it is beginning to take on injection molding for cost performance.

Inside Relativity Space HQ: 3D printer rocket 'factory of the future'
Read more about 3D printing vs CNC machining..
